Bcs Class 2 Drug List Pdf
The Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) is the result of continuous efforts in mathematical analysis for the. The absorption for Class II drugs is.
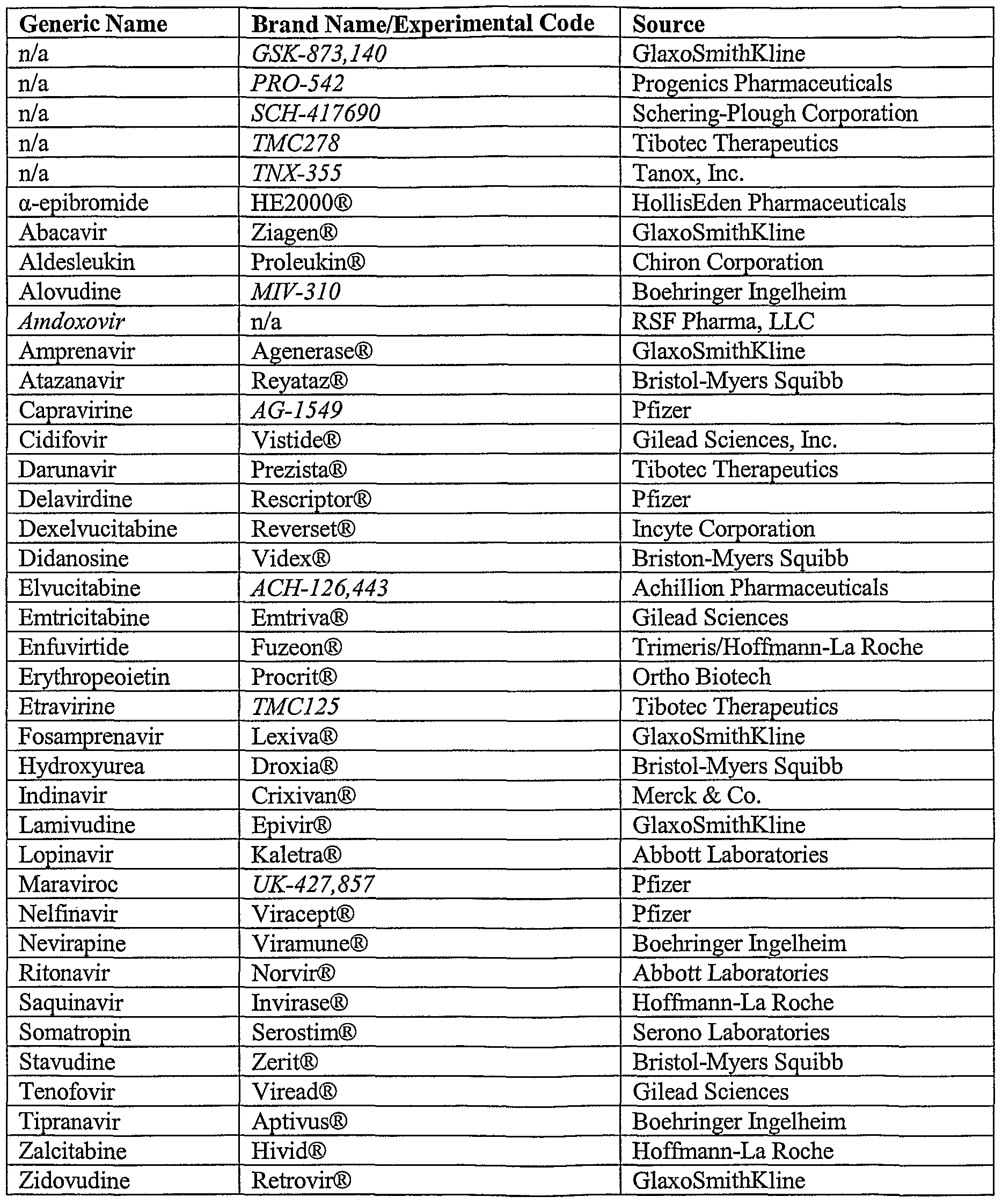
Orally administered, immediate-release (IR) drug products in the top 200 drug product lists from the United States (US), Great Britain (GB), Spain (ES), and Japan (JP) were provisionally classified based on the Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS). The provisional classification is based on the aqueous solubility of the drugs reported in readily available reference literature and a correlation of human intestinal membrane permeability for a set of 29 reference drugs with their calculated partition coefficients. Oral IR drug products constituted more that 50% of the top 200 drug products on all four lists, and ranged from 102 to 113 in number. Drugs with dose numbers less than or equal to unity are defined as high-solubility drugs. More than 50% of the oral IR drug products on each list were determined to be high-solubility drugs (55−59%). The provisional classification of permeability is based on correlations of the human intestinal permeabilities of 29 reference drugs with the calculated Log P or CLogP lipophilicity values for the uncharged chemical form.
Schedule 1 Drug List
The Log P and CLogP estimates were linearly correlated ( r 2 = 0.79) for 187 drugs. Metoprolol was chosen as the reference compound for permeability and Log P or CLogP. A total of 62−69.0% and 56−60% of the drugs on the four lists exhibited CLogP and Log P estimates, respectively, greater than or equal to the corresponding metoprolol value and are provisionally classified as high-permeability drugs.
We have compared the BCS classification in this study with the recently proposed BDDCS classification based on fraction dose metabolism. Although the two approaches are based on different in vivo processes, fraction dose metabolized and fraction dose absorbed are highly correlated and, while depending on the choice of reference drug for permeability classification, e.g., metoprolol vs cimetidine or atenolol, show excellent agreement in drug classification. In summary, more than 55% of the drug products were classified as high-solubility (Class 1 and Class 3) drugs in the four lists, suggesting that in vivo bioequivalence (BE) may be assured with a less expensive and more easily implemented in vitro dissolution test. Keywords: BCS; solubility; dose number; permeability; partition coefficient; WHO essential drugs; top-selling US, European, Japanese drugs; BDDCS.
Contents. BCS classes According to the Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) drug substances are classified to four classes upon their solubility and permeability:. Class I - high, high. Example:.
Those compounds are well absorbed and their absorption rate is usually higher than excretion. Class II - high permeability, low solubility. Example:,. The of those products is limited by their solvation rate. A correlation between the bioavailability and the solvation can be found. Class III - low permeability, high solubility. Example:.
The site has been shut down. Jul 1, 2018 - Instrumen Music Rohani Kristen (2:44:33) - file type: mp3 - download (231.26 MB) - bitrate: 192 kbps. Download Lagu Instrument Piano Rohani. Download free mp3 instrumental rohani kristen.
The absorption is limited by the permeation rate but the drug is solvated very fast. If the formulation does not change the permeability or gastro-intestinal duration time, then class I criteria can be applied. Class IV - low permeability, low solubility. Example:. Those compounds have a poor bioavailability. Usually they are not well absorbed over the intestinal mucosa and a high variability is expected. Definitions The drugs are classified in BCS on the basis of solubility, permeability, and dissolution.

Solubility class boundaries are based on the highest dose strength of an immediate release product. A drug is considered highly soluble when the highest dose strength is soluble in 250 ml or less of aqueous media over the pH range of 1 to 7.5. The volume estimate of 250 ml is derived from typical bioequivalence study protocols that prescribe administration of a drug product to fasting human volunteers with a glass of water. Permeability class boundaries are based indirectly on the extent of absorption of a drug substance in humans and directly on the measurement of rates of mass transfer across human intestinal membrane. Alternatively non-human systems capable of predicting drug absorption in humans can be used (such as in-vitro culture methods).
A drug substance is considered highly permeable when the extent of absorption in humans is determined to be 90% or more of the administered dose based on a mass-balance determination or in comparison to an intravenous dose. For dissolution class boundaries, an immediate release product is considered rapidly dissolving when no less than 85% of the labeled amount of the drug substance dissolves within 15 minutes using USP Dissolution Apparatus 1 at 100 RPM or Apparatus 2 at 50 RPM in a volume of 900 ml or less in the following media: 0.1 N HCl or simulated gastric fluid or pH 4.5 buffer and pH 6.8 buffer or simulated intestinal fluid. See also.
References.